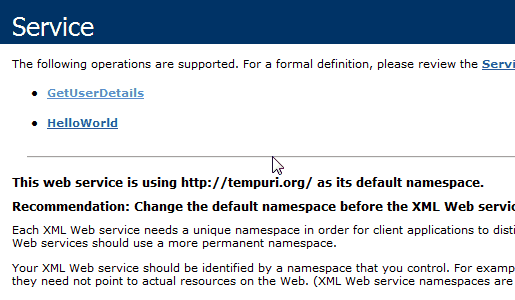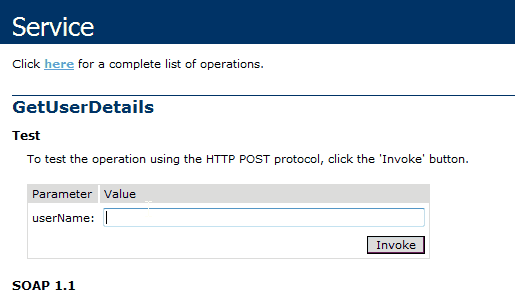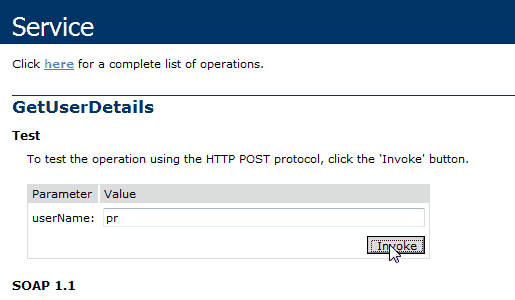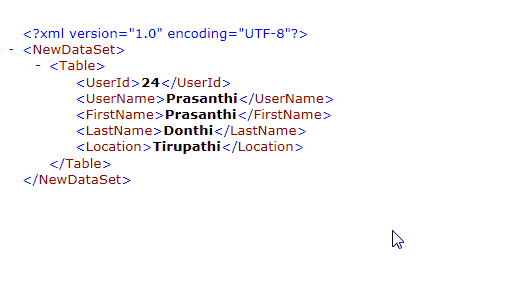
- In C#, two or more methods within the same class can share the same name, as long as their parameter declarations are different.
- These methods are said to be overloaded
- The process is referred to as method overloading.
- Method overloading is one of the ways to implement polymorphism.
- It is not sufficient for two methods to differ only in their return types.
- The methods must differ in the types or number of their parameters.
using System;
class Overload {
public void ovlDemo() {
Console.WriteLine("No parameters");
}
// Overload ovlDemo for one integer parameter.
public void ovlDemo(int a) {
Console.WriteLine("One parameter: " + a);
}
// Overload ovlDemo for two integer parameters.
public int ovlDemo(int a, int b) {
Console.WriteLine("Two parameters: " + a + " " + b);
return a + b;
}
// Overload ovlDemo for two double parameters.
public double ovlDemo(double a, double b) {
Console.WriteLine("Two double parameters: " +
a + " "+ b);
return a + b;
}
}
class MainClass {
public static void Main() {
Overload ob = new Overload();
int resI;
double resD;
// call all versions of ovlDemo()
ob.ovlDemo();
Console.WriteLine();
ob.ovlDemo(2);
Console.WriteLine();
resI = ob.ovlDemo(4, 6);
Console.WriteLine("Result of ob.ovlDemo(4, 6): " +
resI);
Console.WriteLine();
resD = ob.ovlDemo(1.1, 2.32);
Console.WriteLine("Result of ob.ovlDemo(1.1, 2.32): " +
resD); console.WriteLine();
}
}Output:No parameters One parameter: 2 Two parameters: 4 6 Result of ob.ovlDemo(4, 6): 10 Two double parameters: 1.1 2.32 Result of ob.ovlDemo(1.1, 2.32): 3.42
Automatic type conversions can affect overloaded method resolution: int, doubleusing System;
class Overload2 {
public void f(int x) {
Console.WriteLine("Inside f(int): " + x);
}
public void f(double x) {
Console.WriteLine("Inside f(double): " + x);
}
}
class MainClass {
public static void Main() {
Overload2 ob = new Overload2();
int i = 10;
double d = 10.1;
byte b = 99;
short s = 10;
float f = 11.5F;
ob.f(i); // calls ob.f(int)
ob.f(d); // calls ob.f(double)
ob.f(b); // calls ob.f(int) -- type conversion
ob.f(s); // calls ob.f(int) -- type conversion
ob.f(f); // calls ob.f(double) -- type conversion
}
}
Output
Inside f(int): 10 Inside f(double): 10.1 Inside f(int): 99 Inside f(int): 10 Inside f(double): 11.5
Overloaded constructors
Constructor overloading in C# is a type of Static Polymorphism. Using
constructor overloading, any number of constructors can be defined for
the same class. But ensure each constructor must have different number
and type of parameters defined.
public class Car
{
private string make;
private string model;
private string color;
private int yearBuilt;
public Car()
{
this.make = "Ford";
this.model = "Mustang";
this.color = "red";
this.yearBuilt = 1970;
}
public Car(string make)
{
this.make = make;
this.model = "Corvette";
this.color = "silver";
this.yearBuilt = 1969;
}
public Car(string make, string model, string color, int yearBuilt)
{
this.make = make;
this.model = model;
this.color = color;
this.yearBuilt = yearBuilt;
}
public void Display()
{
System.Console.WriteLine("make = " + make);
System.Console.WriteLine("model = " + model);
System.Console.WriteLine("color = " + color);
System.Console.WriteLine("yearBuilt = " + yearBuilt);
}
}
class MainClass
{
public static void Main()
{
Car myCar = new Car("Toyota", "MR2", "black", 1995);
Car myCar2 = new Car();
Car myCar3 = new Car("Chevrolet");
System.Console.WriteLine("myCar details:");
myCar.Display();
System.Console.WriteLine("myCar2 details:");
myCar2.Display();
System.Console.WriteLine("myCar3 details:");
myCar3.Display();
}
}
Output
myCar details: make = Toyota model = MR2 color = black yearBuilt = 1995 myCar2 details: make = Ford model = Mustang color = red yearBuilt = 1970 myCar3 details: make = Chevrolet model = Corvette color = silver yearBuilt = 1969
This example for Constructor Overloading in C# defines three constructors in class "Car".
All the overloaded constructors have the same name as the class name Car
The constructors are invoked during instance creation inside Main method of MainClass.
The constructors are triggered using the new operator followed by the class name and the parameters.
Overriding a method
Method overriding in C# is a feature like the virtual function in C++.
Method overriding is a feature that allows you to invoke functions (that
have the same signatures) that belong to different classes in the same
hierarchy of inheritance using the base class reference. C# makes use of
two keywords: virtual and overrides to accomplish Method overriding.
- Creating a method in derived class with same signature as a method in base class is called as method overriding.
- Same signature means methods must have same name, same number of arguments and same type of arguments.
- Method overriding is possible only in derived classes, but not within the same class.
- When derived class needs a method with same signature as in base class, but wants to execute different code than provided by base class then method overriding will be used.
- To allow the derived class to override a method of the base class, C# provides two options, virtual methods and abstract methods.
using System;
public class Employee {
private int fAge;
public Employee() {
fAge = 21;
}
public virtual void setAge(int age) {
fAge = age;
}
public virtual int getAge() {
return fAge;
}
}
public class AdultEmployee : Employee {
public AdultEmployee() {
}
override public void setAge(int age) {
if (age > 21)
base.setAge(age);
}
}
class MainClass {
public static void Main() {
Employee p = new Employee();
p.setAge(18);
AdultEmployee ap = new AdultEmployee();
ap.setAge(18);
Console.WriteLine("Employee Age: {0}", p.getAge());
Console.WriteLine("AdultEmployee Age: {0}", ap.getAge());
}
}